Polyurethane Foam Properties & Certified Standards
What are the standard properties of polyurethane foam? Today’s article will cover 5 fundamental characteristics of PU and 8 testing standards to consider.
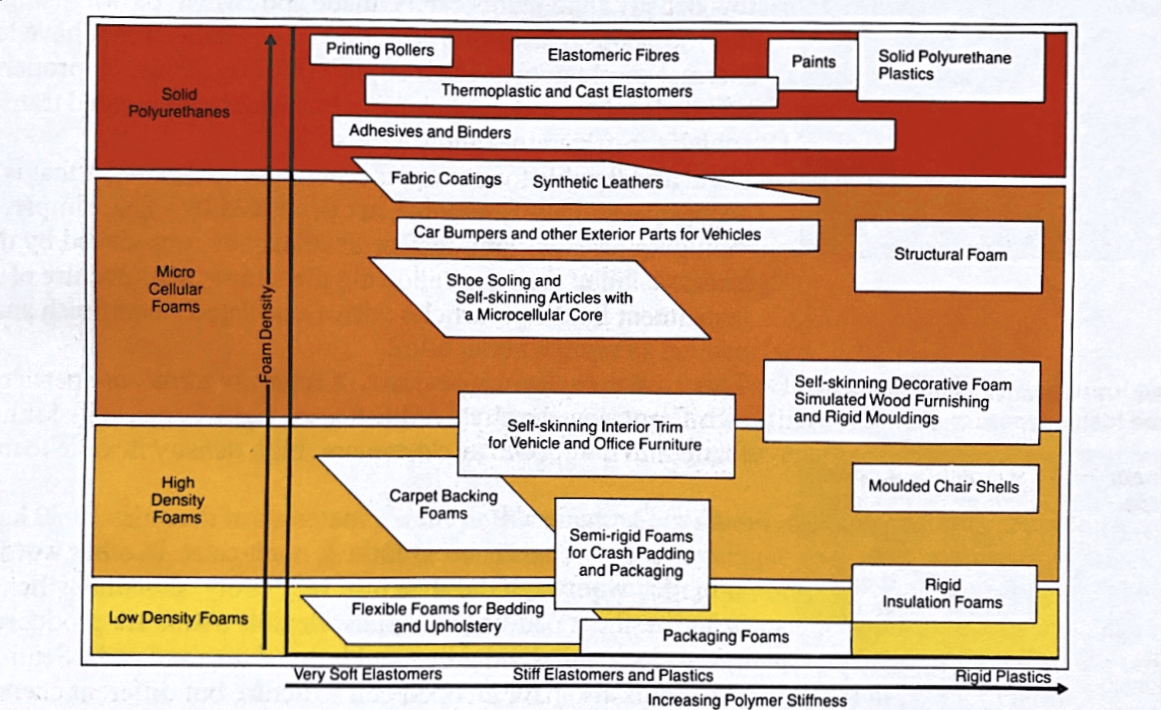
Foam Density
Foam density is probably the most frequently dealt-with property in the PU industry. When you order with Sunkist, we send you a questionnaire that includes a question about foam density. This is because foam density is an integral element in both foaming and cutting operations—failing to consider it can not only damage your product, but also your machines.
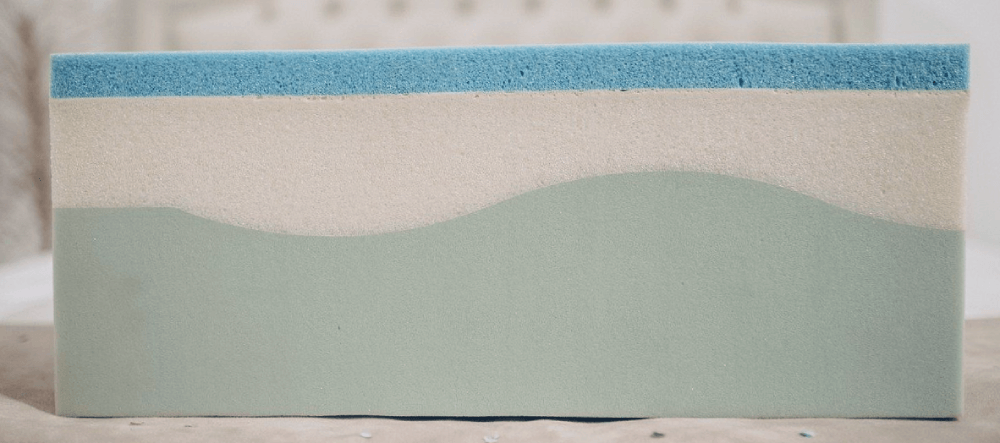

What we typically refer to as “low density foam” is the most common material for bedding and upholstery. Think squishy, bendy foam in quilted materials, shoulder pads, etc. “High density foam” tends to refer to things like carpet backing foam or rigid mouldings for things like furniture and decor.
Now you may have noticed, there seems to be a big difference between pliable carpet backing foam and rigid moulded furniture.
That brings us to the next important foam property: polymer stiffness.
Polymer Stiffness
Sometimes people equate foam density with stiffness because the perception is that denser foam is stiffer, while less dense foam is more flexible. This can be true, but is not always the case.
Compare rigid insulation foam, a low density foam, to carpet backing, a high density foam. The rigid foam board is stiffer, while the carpet backing is denser, but far less stiff.

Material stiffness has to do with foam structure. Basically, PU foam rises like a sponge cake filled with air bubbles. If you break the walls of those air bubbles before they stiffen, you get open-cell foam. If you leave the walls to stiffen (and don’t crush it afterward), you get closed-cell foam. Open-cell foams are flexible, while closed-cell foams are rigid. You can have low and high density foam with open or closed cells.
Adhesion
While forming, polyurethane foam is adhesive. This is why backing paper is necessary in slabstock and box foaming. This is also why you can select from Sunkist’s range of laminating machines, which let you save on money by eliminating the use of additional adhesives simply by using the PU’s own adhesion. You’ll also find PU adhesion being utilized in spray foam products.
Insulation
Low density rigid foams in particular have very low thermal conductivity, meaning they make for great insulators. That’s why you’ll find rigid foam boards in architecture stacked between walls. You’ll also find rigid foam in refrigeration; effective insulation lowers the amount of energy necessary to keep the inside of a refrigerator cool, so can save consumers money in the long run.
Abrasion Resistance
Finally, let’s talk about abrasion-resistant foam. High density flexible foams are made into upholstery parts, vehicle trims, and shoe-soling because they are self-skinning, meaning they produce an outer “skin” of much higher density than the interior. This skin is not only abrasion-resistant, but also decorative, as it can be made to look like wood, imitation leather, etc. This PU foam property is of particular importance to the footwear industry, as PU elastomer shoe soles provide both flexibility and hardiness for effective use.
A Quick List of Physical-Mechanical Properties
The five properties above are industry colloquial standards when classifying foam. Now let’s quickly cover the internationally recognized standards that foams are tested and certified by.
- Density
- How dense is your foam?
- ISO 1855 / UNI 6349 / DIN 53420
- Indentation Deflection
- How much weight does it take to indent your foam?
- ISO 2439 / UNI 6353 / DIN 53576/B
- Compression Load Deflection
- How much pressure is needed to compress your foam?
- ISO 3386 / UNI 6351 / DIN 53577
- Tensile Strength and Elongation at Break
- How much can your foam stretch?
- DIN 53571
- Compression Set
- How much volume does your foam lose when compressed?
- UNI 6352 / DIN 53572
- Dynamic Fatigue
- How much can your foam recover and bounce back under dynamic conditions?
- UNI 6356 pt. 2
- Resilience
- How much does your foam bounce?
- UNI 6357
- Air Permeability
- How much air flow can go through your foam?
- No testing standard yet
Want more information? Visit Olmo Group’s fantastic guidebook here.
Conclusion
Expand your business repertoire by learning the fundamental properties of polyurethane foam. Some consumer markets prefer certified foam to ensure performance. Are you a manufacturer interested in certifying your products? Inquire about Sunkist’s “For Laboratory” machinery line to learn more.

Want to keep up to date on our company news? Take 1 minute to fill out the form below.